Serializando datos
Cuando hablamos de serialización, nos referimos tanto a la serialización de datos como a la deserialización de datos.
La serialización entra en juego en algunos puntos a lo largo del ciclo de vida de las cuentas del programa y los programa en Solana:
- Serialización de datos de instrucciones en el cliente
- Deserializar datos de instrucción en el programa
- Serialización de datos de la cuenta en el programa
- Deserialización de datos de cuenta en el cliente
Es importante que todas las acciones anteriores estén respaldadas por el mismo enfoque de serialización. Los fragmentos (snippets) incluidos demuestran la serialización mediante Borsh.
Los ejemplos en el resto de este documento son extractos tomados de la Plantilla del programa CLI de Solana
Configuración para la serialización con Borsh
Las bibliotecas para Borsh deben configurarse para el programa Rust, el cliente Rust, el cliente Node y/o Python.
[package]
name = "solana-cli-template-program-bpf"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[features]
no-entrypoint = []
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
num-derive = "0.3"
num_enum = "0.5.1"
num-integer = "0.1.44"
num-traits = "0.2"
sol-template-shared = {path = "../shared"}
solana-program = "1.8.2"
thiserror = "1.0"
[dev-dependencies]
solana-program-test = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
[lib]
crate-type = ["cdylib", "lib"]
[package]
name = "cli-program-template"
version = "0.1.5"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
publish = false
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
clap = "2.33.3"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
serde = { version = "1.0.125", features = ["derive"] }
serde_yaml = "0.8.17"
sol-template-shared = {path = "shared"}
solana-clap-utils = "1.8.2"
solana-cli-config = "1.8.2"
solana-client = "1.8.2"
solana-logger = "1.8.2"
solana-remote-wallet = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full"] }
[workspace]
members = [
"program",
"shared",
]
[dev-dependencies]
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
solana-validator = "1.8.2"
solana-streamer = "1.8.2"
{
"name": "ts-program-template",
"version": "0.1.0",
"description": "Sample TS App",
"main": "client/nmain.ts",
"author": "",
"keywords": [],
"workspace": "client/",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template"
},
"homepage": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template",
"scripts": {
"test:all": "npm run build:client && npm run test:client",
"build:client": "rm -rf ./.dist/client && tsc ",
"start": "node ./node_modules/.bin/mocha .dist/client/main.js",
"test:client": "npm run start",
"lint": "eslint --ext .ts client/* && prettier --check \"client/**/*.ts\"",
"lint:fix": "eslint --ext .ts client/* --fix",
"pretty": "prettier --write '{,client/**/}*.ts'"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@tsconfig/recommended": "^1.0.1",
"@types/chai": "^4.3.0",
"@types/eslint": "^7.28.2",
"@types/eslint-plugin-prettier": "^3.1.0",
"@types/mkdirp": "^1.0.2",
"@types/mocha": "^9.0.0",
"@types/prettier": "^2.4.1",
"@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin": "^5.6.0",
"@typescript-eslint/parser": "^5.6.0",
"chai": "^4.3.4",
"eslint": "^8.2.0",
"eslint-config-google": "^0.14.0",
"eslint-config-prettier": "^8.3.0",
"eslint-plugin-prettier": "^4.0.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^5.5.0",
"mocha": "^9.1.3",
"prettier": "^2.4.1",
"start-server-and-test": "^1.14.0",
"ts-node": "^10.4.0",
"typescript": "^4.5.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"@solana/web3.js": "^1.31.0",
"borsh": "^0.7.0",
"env": "^0.0.2",
"fs": "^0.0.1-security",
"mkdirp": "^1.0.4",
"npm-check-updates": "^12.0.3",
"sync-request": "^6.1.0",
"update": "^0.4.2"
}
}
borsh-construct==0.1.0
solana==0.20.0
Cómo serializar datos de instrucciones en el cliente
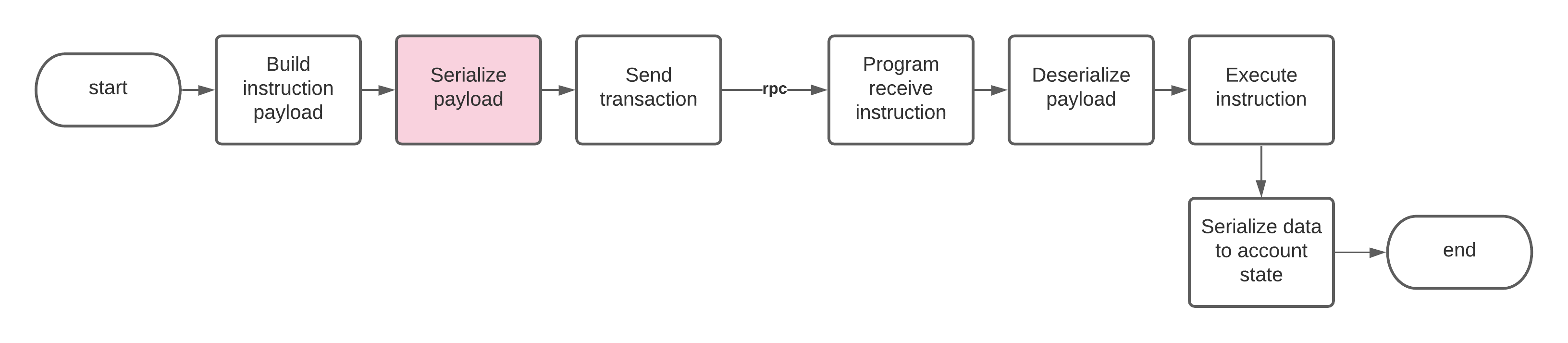
Si está serializando datos de instrucciones de salida para enviar a un programa, debe reflejar cómo el programa deserializa el datos de instrucciones entrantes.
En esta plantilla, un bloque de datos de instrucción es una matriz serializada que contiene, con ejemplos:
| Instrucción (Índice variable) | Llave serializada | Valor serializado |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize (0) | no aplica para la instrucción | no aplica para la instrucción |
| Mint (1) | "foo" | "bar" |
| Transfer (2) | "foo" | no aplica para la instrucción |
| Burn (2) | "foo" | no aplica para la instrucción |
En el siguiente ejemplo, asumimos que la cuenta propiedad del programa se ha inicializado
// Include borsh functionality
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
// Get Solana
import {
Keypair,
Connection,
PublicKey,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
// Our instruction payload vocabulary
class Payload extends Assignable {}
// Borsh needs a schema describing the payload
const payloadSchema = new Map([
[
Payload,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["id", "u8"],
["key", "string"],
["value", "string"],
],
},
],
]);
// Instruction variant indexes
enum InstructionVariant {
InitializeAccount = 0,
MintKeypair,
TransferKeypair,
BurnKeypair,
}
/**
* Mint a key value pair to account
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} progId - Sample Program public key
* @param {PublicKey} account - Target program owned account for Mint
* @param {Keypair} wallet - Wallet for signing and payment
* @param {string} mintKey - The key being minted key
* @param {string} mintValue - The value being minted
* @return {Promise<Keypair>} - Keypair
*/
export async function mintKV(
connection: Connection,
progId: PublicKey,
account: PublicKey,
wallet: Keypair,
mintKey: string,
mintValue: string
): Promise<string> {
// Construct the payload
const mint = new Payload({
id: InstructionVariant.MintKeypair,
key: mintKey, // 'ts key'
value: mintValue, // 'ts first value'
});
// Serialize the payload
const mintSerBuf = Buffer.from(serialize(payloadSchema, mint));
// console.log(mintSerBuf)
// => <Buffer 01 06 00 00 00 74 73 20 6b 65 79 0e 00 00 00 74 73 20 66 69 72 73 74 20 76 61 6c 75 65>
// let mintPayloadCopy = deserialize(schema, Payload, mintSerBuf)
// console.log(mintPayloadCopy)
// => Payload { id: 1, key: 'ts key', value: 'ts first value' }
// Create Solana Instruction
const instruction = new TransactionInstruction({
data: mintSerBuf,
keys: [
{ pubkey: account, isSigner: false, isWritable: true },
{ pubkey: wallet.publicKey, isSigner: false, isWritable: false },
],
programId: progId,
});
// Send Solana Transaction
const transactionSignature = await sendAndConfirmTransaction(
connection,
new Transaction().add(instruction),
[wallet],
{
commitment: "singleGossip",
preflightCommitment: "singleGossip",
}
);
console.log("Signature = ", transactionSignature);
return transactionSignature;
}
from borsh_construct import String, CStruct, U8
from enum import IntEnum
from solana.transaction import Transaction
from solders.pubkey import Pubkey
from solders.keypair import Keypair
from solders.instruction import Instruction, AccountMeta
from solders.rpc.responses import SendTransactionResp
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Instruction variants for target program
class InstructionVariant(IntEnum):
INITIALIZE = 0
MINT = 1
TRANSFER = 2
BURN = 3
# Schema for sending instructionVariants to on-chain sample program
payload_schema = CStruct("id" / U8, "key" / String, "value" / String)
def construct_payload(instruction_variant: InstructionVariant, key: str, value: str):
"""Generate a serialized instructionVariant"""
return payload_schema.build({"id": instruction_variant, "key": key, "value": value})
def mint_kv(
client: Client,
program_pk: Pubkey,
account_pk: Pubkey,
wallet_kp: Keypair,
mint_key: str,
mint_value: str,
) -> SendTransactionResp:
"""Mint with a key/value pair to an account"""
# Construct the program payload for Mint invariant
payload_ser = construct_payload(InstructionVariant.MINT, mint_key, mint_value)
# print(payload_ser)
# => b'\x01\n\x00\x00\x00python key\x0c\x00\x00\x00python value'
# mint_payload_copy = payload_schema.parse(payload_ser)
# print(mint_payload_copy)
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => key = u'python key' (total 10)
# => value = u'python value' (total 12)
# Construct the transaction with instructionVariant
txn = Transaction().add(
Instruction(
accounts=[AccountMeta(account_pk, False, True)], program_id=program_pk, data=payload_ser
)
)
return client.send_transaction(txn, wallet_kp)
# => {'jsonrpc': '2.0', 'result': '4ZdpWNdovdVaLextWSiqEBWp67k9rNTTUaX3qviHDXWY9c98bVtaRt5sasPhYzMVXHqhex78gzNKytcBnVH5CSTZ', 'id': 2}
/// Instruction payload gets serialized
#[derive(BorshSerialize)]
pub struct Payload<'a> {
variant: u8,
key: &'a str,
value: &'a str,
}
/// Perform a mint transaction consisting of a key/value pair
/// See submit_transaction below
pub fn mint_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
accounts: &[AccountMeta],
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
mint_key: &str,
mint_value: &str,
mint_instruction_id: u8,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Setup the payload. `mint_instruction_id` is instruction variant index = 1
let data = Payload<`_> {
variant: mint_instruction_id,
key: mint_key,
value: mint_value,
};
let instruction = Instruction::new_with_borsh(PROG_KEY.pubkey(), &data, accounts.to_vec());
submit_transaction(rpc_client, wallet_signer, instruction, commitment_config)
}
/// Submits the program instruction as per the
/// instruction definition
pub fn submit_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
instruction: Instruction,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let mut transaction =
Transaction::new_unsigned(Message::new(&[instruction], Some(&wallet_signer.pubkey())));
let (recent_blockhash, _fee_calculator) = rpc_client
.get_recent_blockhash()
.map_err(|err| format!("error: unable to get recent blockhash: {}", err))?;
transaction
.try_sign(&vec![wallet_signer], recent_blockhash)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: failed to sign transaction: {}", err))?;
let signature = rpc_client
.send_and_confirm_transaction_with_spinner_and_commitment(&transaction, commitment_config)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: send transaction: {}", err))?;
Ok(signature)
}
How to deserialize instruction data on the program
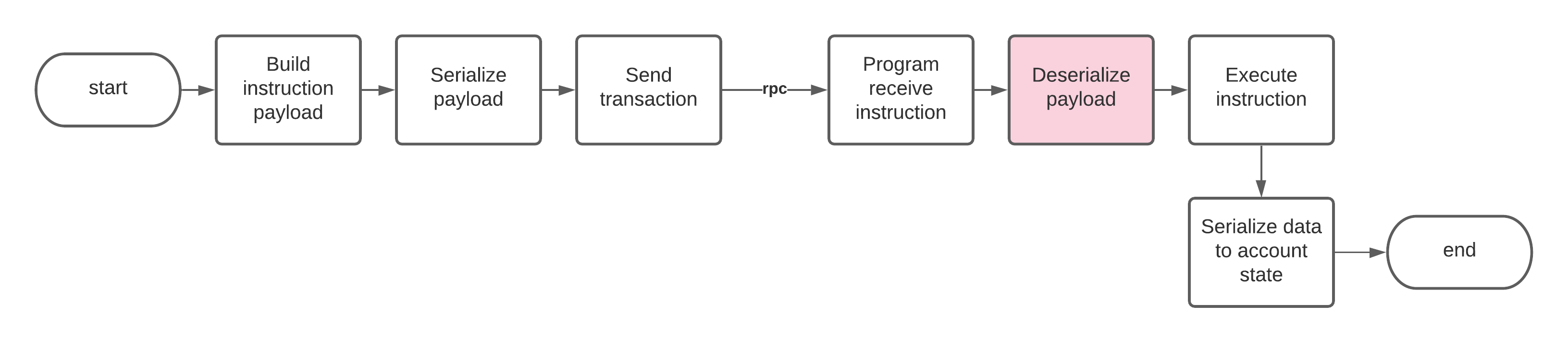
//! instruction Contains the main ProgramInstruction enum
use {
crate::error::SampleError, borsh::BorshDeserialize, solana_program::program_error::ProgramError,
};
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq)]
/// All custom program instructions
pub enum ProgramInstruction {
InitializeAccount,
MintToAccount { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccounts { key: String },
BurnFromAccount { key: String },
MintToAccountWithFee { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: String },
BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: String },
}
/// Generic Payload Deserialization
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, Debug)]
struct Payload {
variant: u8,
arg1: String,
arg2: String,
}
impl ProgramInstruction {
/// Unpack inbound buffer to associated Instruction
/// The expected format for input is a Borsh serialized vector
pub fn unpack(input: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
let payload = Payload::try_from_slice(input).unwrap();
match payload.variant {
0 => Ok(ProgramInstruction::InitializeAccount),
1 => Ok(Self::MintToAccount {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
2 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccounts { key: payload.arg1 }),
3 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccount { key: payload.arg1 }),
4 => Ok(Self::MintToAccountWithFee {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
5 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
6 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
_ => Err(SampleError::DeserializationFailure.into()),
}
}
}
Cómo serializar los datos de la cuenta en el programa
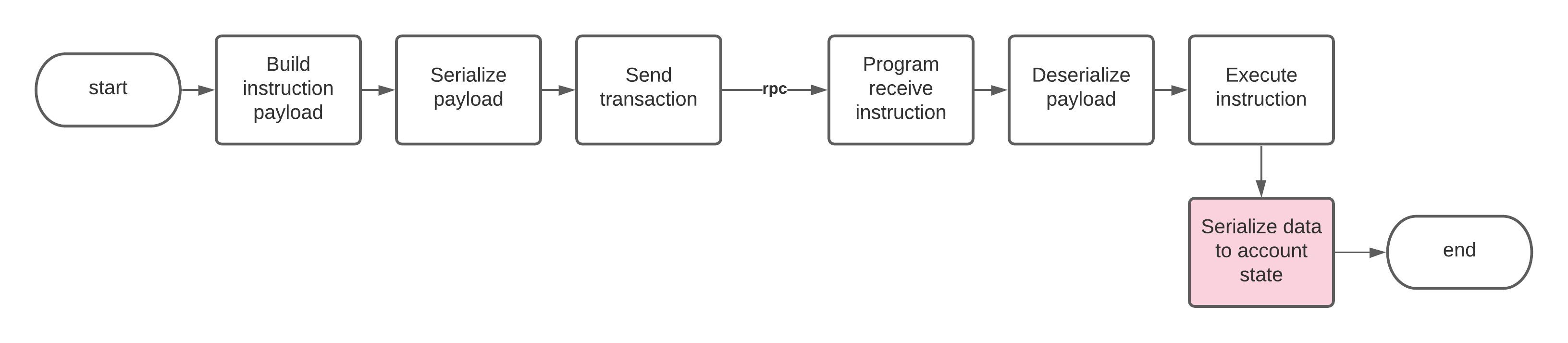
El bloque de datos de la cuenta del programa (como se ve en el repositorio) está estructurado de la siguiente manera:
| Byte 0 | Bytes 1-4 | Bytes hasta 1019 |
|---|---|---|
| bandera de inicializado | longitud del BTreeMap serializado | BTreeMap (donde los pares clave/valor son almacenados) |
Pack
Unas palabras sobre el trait Pack
El trait Pack hace que sea más fácil ocultar los detalles de la serialización/deserialización de los datos de la cuenta en el procesamiento de instrucciones de su programa principal. En lugar de poner la serialización/deserialización en el código del programa, encapsula los detalles por detrás de (3) funciones:
unpack_unchecked- Le permite deserializar una cuenta sin validar si se ha inicializado. Es útil cuando realmente está procesando la función de inicialización (índice 0)unpack- LLama a tu implementación deunpack_from_slicey valida si la cuenta se ha inicializado.pack- LLama a tu implementación depack_into_slice
Here is the implementation of the Pack trait for our sample program. This is followed with the actual processing of the account data using borsh.
Aquí está la implementación del trait Pack para nuestro programa de ejemplo. Seguido del procesamiento actual de la cuenta usando borsh.
//! @brief account_state manages account data
use crate::error::SampleError;
use sol_template_shared::ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
use solana_program::{
entrypoint::ProgramResult,
program_error::ProgramError,
program_pack::{IsInitialized, Pack, Sealed},
};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
/// Maintains global accumulator
#[derive(Debug, Default, PartialEq)]
pub struct ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: BTreeMap<String, String>,
}
impl ProgramAccountState {
/// Returns indicator if this account has been initialized
pub fn set_initialized(&mut self) {
self.is_initialized = true;
}
/// Adds a new key/value pair to the account
pub fn add(&mut self, key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(&key) {
true => Err(SampleError::KeyAlreadyExists.into()),
false => {
self.btree_storage.insert(key, value);
Ok(())
}
}
}
/// Removes a key from account and returns the keys value
pub fn remove(&mut self, key: &str) -> Result<String, SampleError> {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(key) {
true => Ok(self.btree_storage.remove(key).unwrap()),
false => Err(SampleError::KeyNotFoundInAccount),
}
}
}
impl Sealed for ProgramAccountState {}
// Pack expects the implementation to satisfy whether the
// account is initialzed.
impl IsInitialized for ProgramAccountState {
fn is_initialized(&self) -> bool {
self.is_initialized
}
}
impl Pack for ProgramAccountState {
const LEN: usize = ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
/// Store 'state' of account to its data area
fn pack_into_slice(&self, dst: &mut [u8]) {
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice(self.is_initialized, &self.btree_storage, dst);
}
/// Retrieve 'state' of account from account data area
fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
match sol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice(src) {
Ok((is_initialized, btree_map)) => Ok(ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized,
btree_storage: btree_map,
}),
Err(_) => Err(ProgramError::InvalidAccountData),
}
}
}
Serialización/Deserealización
Para completar la serialización y deserialización internamente:
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice- Donde la serialización ocurre realmentesol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice- Donde la deserialización ocurre realmente
Ten en cuenta que tenemos una partición u32 (4 bytes) en el diseño de datos para BTREE_LENGTH que precede a BTREE_STORAGE. Esto se debe a que borsh, durante la deserialización, comprueba que la longitud del segmento que está deserializando coincide con la cantidad de datos que lee antes de la recombinación real del objeto receptor. El enfoque que se muestra a continuación primero lee BTREE_LENGTH para obtener el tamaño para hacer slice del puntero BTREE_STROAGE.
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
solana_program::program_memory::sol_memcpy,
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
/// Initialization flag size for account state
pub const INITIALIZED_BYTES: usize = 1;
/// Storage for the serialized size of the BTreeMap control
pub const BTREE_LENGTH: usize = 4;
/// Storage for the serialized BTreeMap container
pub const BTREE_STORAGE: usize = 1019;
/// Sum of all account state lengths
pub const ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE: usize = INITIALIZED_BYTES + BTREE_LENGTH + BTREE_STORAGE;
/// Packs the initialized flag and data content into destination slice
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn pack_into_slice(
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: &BTreeMap<String, String>,
dst: &mut [u8],
) {
let dst = array_mut_ref![dst, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_dst, data_len_dst, data_dst) =
mut_array_refs![dst, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
// Set the initialized flag
is_initialized_dst[0] = is_initialized as u8;
// Store the core data length and serialized content
let keyval_store_data = btree_storage.try_to_vec().unwrap();
let data_len = keyval_store_data.len();
if data_len < BTREE_STORAGE {
data_len_dst[..].copy_from_slice(&(data_len as u32).to_le_bytes());
sol_memcpy(data_dst, &keyval_store_data, data_len);
} else {
panic!();
}
}
/// Unpacks the data from slice and return the initialized flag and data content
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Usage
Lo siguiente es el consolidado y demuestra cómo el programa interactúa con ProgramAccountState que encapsula el indicador de inicialización, así como el BTreeMap interno para nuestros pares clave/valor.
Primero cuando queremos inicializar una cuenta nueva:
/// Initialize a new program account, which is the first in AccountInfo array
fn initialize_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo]) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Initialize account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Here we use unpack_unchecked as we have yet to initialize
// Had we tried to use unpack it would fail because, well, chicken and egg
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack_unchecked(&account_data)?;
// We double check that we haven't already initialized this accounts data
// more than once. If we are good, we set the initialized flag
if account_state.is_initialized() {
return Err(SampleError::AlreadyInitializedState.into());
} else {
account_state.set_initialized();
}
// Finally, we store back to the accounts space
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data).unwrap();
Ok(())
}
Ahora podemos operar en nuestras otras instrucciones como se puede apreciar al hacer mint de un nuevo par clave/valor que anteriormente demostramos cuando enviamos instrucciones desde un cliente:
/// Mint a key/pair to the programs account, which is the first in accounts
fn mint_keypair_to_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo], key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Mint to account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Unpacking an uninitialized account state will fail
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack(&account_data)?;
// Add the key value pair to the underlying BTreeMap
account_state.add(key, value)?;
// Finally, serialize back to the accounts data
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data)?;
Ok(())
}
Cómo deserializar los datos de la cuenta en el cliente
Los clientes pueden llamar a Solana para obtener la cuenta propiedad del programa, en la que la respuesta es un bloque de datos serializado. La deserialización requiere conocer la estructura del bloque de datos.
La estructura del bloque de datos se muestra aquí
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import {
Keypair,
AccountMeta,
Connection,
LAMPORTS_PER_SOL,
PublicKey,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
export class AccoundData extends Assignable {}
const dataSchema = new Map([
[
AccoundData,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["initialized", "u8"],
["tree_length", "u32"],
["map", { kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" }],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Fetch program account data
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} account - Public key for account whose data we want
* @return {Promise<AccoundData>} - Keypair
*/
export async function getAccountData(
connection: Connection,
account: PublicKey
): Promise<AccoundData> {
let nameAccount = await connection.getAccountInfo(account, "processed");
return deserializeUnchecked(dataSchema, AccoundData, nameAccount.data);
}
from borsh_construct import CStruct, U8, U32, HashMap, String
from solana.rpc.commitment import Confirmed
from solders.pubkey import Pubkey
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Schema to deserialize program's account data
account_schema = CStruct(
"initialized" / U8,
"map_length" / U32,
"map" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def get_account_info(client: Client, account_pk: Pubkey):
"""Fetch account information from RPC, parse out the data and deserialize"""
res = client.get_account_info(account_pk, Confirmed, encoding='base64')
return account_schema.parse(res.value.data)
# Results in or similar
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => map_length = 109
# => map = {'Happy': 'New Year!', 'newKey': 'A new value',
# => 'python key': 'python value', 'ts key': 'ts first value'}
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Mappins comunes de Solana TS/JS
La especificación de Borsh contiene la mayoría de los mapeos para primitivos y tipos de datos compuestos.
La clave para TS/JS y Python es crear un esquema de Borsh con una definición adecuada para que la serialización y deserialización puede generar o recorrer las respectivas entradas.
Aquí demostramos la serialización de primitivos (números, cadenas) y tipos compuestos (matriz de tamaño fijo, Map) primero en Typescript, luego en Python y luego la deserialización equivalente en el lado de Rust:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { expect } from "chai";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* Primitive extends the Struct type from Solana Library
* for convenience of dynamic property setting
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
*/
class Primitive extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
}
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry() {
// Emulate BTreeMap
let map = new Map();
map.set("cookbook", "recipe");
map.set("recipe", "ingredient");
// Setup a Primitive for all basic and a few
// compound types
const value = new Primitive({
U8: 255,
U16: 65535,
U32: 4294967295,
FIXED_STRING_ARRAY: ["hello", "world"],
FIXED_U8_ARRAY: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
MAP_STRING_STRING: map,
});
// Define our schema
const schema = new Map([
[
Primitive,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["U8", "u8"],
["U16", "u16"],
["U32", "u32"],
["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY", ["string", 2]],
["FIXED_U8_ARRAY", ["u8", 5]],
[
"MAP_STRING_STRING",
{ kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" },
],
],
},
],
]);
console.log("Value = ", value);
// Serialize then deserialize
const dser = Buffer.from(serialize(schema, value));
console.log(dser);
const newValue = deserialize(schema, Primitive, dser);
// Viola!
console.log("New value = ", newValue);
console.log("Fixed string array = ", newValue["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Fixed u8 array = ", newValue["FIXED_U8_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Map = ", newValue["MAP_STRING_STRING"]);
}
entry();
from borsh_construct import U8, U16, U32, String, HashMap
# Schema to deserialize various types
primitive_schema = CStruct(
"U8" / U8,
"U16" / U16,
"U32" / U32,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY" / String[2],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY" / U8[5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def common():
mapping = {"cookbook": "recipe", "recipe": "ingredient"}
# Serialize
dser = primitive_schema.build({
'U8': 255,
'U16': 65535,
'U32': 4294967295,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY": ['hello', 'world'],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING": mapping})
print(dser)
# => b'\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\x05\x00\x00\x00hello\x05\x00\x00\x00world\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x02\x00\x00\x00\x08\x00\x00\x00cookbook\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\n\x00\x00\x00ingredient'
# Deserialize
new_value = primitive_schema.parse(dser)
# Viola
print(new_value)
# => Container:
# => U8 = 255
# => U16 = 65535
# => U32 = 4294967295
# => FIXED_STRING_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => hello
# => world
# => FIXED_U8_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => 1
# => 2
# => 3
# => 4
# => 5
# => MAP_STRING_STRING = {'cookbook': 'recipe', 'recipe': 'ingredient'}
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
#[test]
fn primitives() {
let prim = [
255u8, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 5, 0, 0, 0, 104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 5, 0, 0, 0,
119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 99, 111, 111, 107, 98,
111, 111, 107, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105, 112, 101, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105,
112, 101, 10, 0, 0, 0, 105, 110, 103, 114, 101, 100, 105, 101, 110, 116,
];
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct Primitive(
u8,
u16,
u32,
String,
String,
[u8; 5],
BTreeMap<String, String>,
);
let x = Primitive::try_from_slice(&prim).unwrap();
println!("{:?}", x);
}
}
Construcciones avanzadas
Hemos mostrado cómo crear cargas útiles simples en ejemplos anteriores. Algunas veces Solana lanza una bola rápida con ciertos tipos. Esta sección demostrará el mapeo adecuado entre TS/JS y Rust para manejar esos casos:
COption
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* COption is meant to mirror the
* `solana_program::options::COption`
*
* This type stores a u32 flag (0 | 1) indicating
* the presence or not of a underlying PublicKey
*
* Similar to a Rust Option
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
* @implements {encode}
*/
class COption extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
/**
* Creates a COption from a PublicKey
* @param {PublicKey?} akey
* @returns {COption} COption
*/
static fromPublicKey(akey?: PublicKey): COption {
if (akey == undefined) {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 0,
pubKeyBuffer: new Uint8Array(32),
});
} else {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 1,
pubKeyBuffer: akey.toBytes(),
});
}
}
/**
* @returns {Buffer} Serialized COption (this)
*/
encode(): Buffer {
return Buffer.from(serialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this));
}
/**
* Safe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decode(data): COption {
return deserialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
/**
* Unsafe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decodeUnchecked(data): COption {
return deserializeUnchecked(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
}
/**
* Defines the layout of the COption object
* for serializing/deserializing
* @type {Map}
*/
const COPTIONSCHEMA = new Map([
[
COption,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["noneOrSome", "u32"],
["pubKeyBuffer", [32]],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry(indata?: PublicKey) {
// If we get a PublicKey
if (indata) {
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey(indata);
console.log("Testing COption with " + indata.toBase58());
// Serialize it
let copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log("copt_ser ", copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone);
// Validate contains PublicKey
if (tdone["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
console.log("pubkey: " + new PublicKey(tdone["pubKeyBuffer"]).toBase58());
}
/*
Output:
Testing COption with A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
copt_ser Buffer(36) [1, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186, 109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 1064, length: 36]
COption {noneOrSome: 1, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32)}
pubkey: A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
*/
} else {
console.log("Testing COption with null");
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey();
// Serialize it
const copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log(copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone1 = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone1);
// Validate does NOT contains PublicKey
if (tdone1["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
throw Error("Expected no public key");
} else console.log("pubkey: null");
/*
Output:
Testing COption with null
Buffer(36)[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 2272, length: 36]
COption { noneOrSome: 0, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32) }
pubkey: null
*/
}
}
// Test with PublicKey
entry(new PublicKey("A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU"));
console.log("");
// Test without PublicKey
entry();
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use arrayref::{array_ref, array_refs};
use solana_program::{program_option::COption, pubkey::Pubkey};
/// Emulate how COption is 'unpacked'
fn deser_option(data: &[u8]) -> COption<Pubkey> {
// Map the data block
let ain = array_ref![data, 0, 36];
let (base, key) = array_refs![ain, 4, 32];
// Get the SOME or NONE u32
let nos = u32::from_le_bytes(*base);
// Construct the COption accordingly
let opt: COption<Pubkey> = if nos == 0 {
COption::None
} else {
COption::Some(Pubkey::new_from_array(*key))
};
opt
}
#[test]
fn btest() {
// From Typescript with borsh'ing
let copt = [
1u8, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186,
109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35,
];
// Emulate COption deserialization
let coption = deser_option(&copt);
if coption.is_some() {
println!("{:?}", coption.expect("Uh-oh"));
}
// As a Borsh Struct
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct TOption(u32, [u8; 32]);
let toption = TOption::try_from_slice(&copt).unwrap();
let pkey = Pubkey::new_from_array(toption.1);
println!("Some = {:?} Pubkey = {:?}", toption.0, pkey);
}
}